3D Shapes Explained: A Fun Geometry Guide for Students | Studit
Geometry is everywhere, from the soccer ball you kick to the juice can you drink from! At Studit, we make learning about 3D shapes fun and easy for students in Classes 1 to 12, whether you’re studying for CBSE, ICSE, CHSE, or state board exams. In this guide, we’ll explore what 3D shapes are, their types, properties, and how they appear in real life. Ready to dive into the world of solids? Let’s get started with Studit’s expert tutoring!
Table of Contents
- What Are 3D Shapes?
- Types of 3D Shapes
- Properties of 3D Shapes
- Surface Area and Volume of 3D Shapes
- 3D Shapes and Nets
- Solved Examples
- Learn Geometry with Studit
What Are 3D Shapes?
3D shapes, also called solids, are objects that have three dimensions: length, width, and height. Unlike flat 2D shapes (like a circle or square), 3D shapes have depth, making them solid objects you can hold, like a ball or a box. In geometry, 3D shapes are defined by their faces (flat or curved surfaces), edges (lines where faces meet), and vertices (points where edges meet).
You see 3D shapes every day! Think of a basketball (sphere), a juice can (cylinder), or an ice cream cone (cone). Understanding 3D shapes is key for CBSE, ICSE, and state board math exams, and Studit’s tutors in Bhubaneswar are here to help you master them!

Types of 3D Shapes
3D shapes can be divided into two main types: polyhedrons (with flat, straight-sided faces) and curved solids (with curved surfaces). Let’s explore the most common ones:
Polyhedrons
Polyhedrons are 3D shapes with flat faces and straight edges. Here are some examples:
- Cube: A 3D shape with 6 equal square faces, like a Rubik’s Cube or a dice.

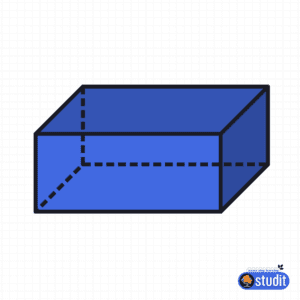
- Cuboid: A 3D shape with 6 rectangular faces, like a shoebox or a book.

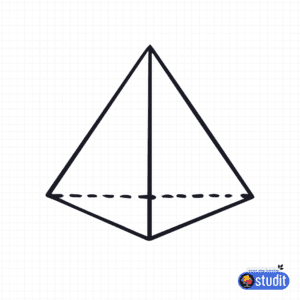
- Pyramid: A 3D shape with a polygon base (e.g., square or triangle) and triangular faces meeting at a point called the apex, like the pyramids in Egypt.

- Prism: A 3D shape with two identical polygon bases connected by flat faces, like a triangular prism (used in optics) or a rectangular prism (like a cereal box).

Curved Solids
Curved solids have at least one curved surface. Examples include:
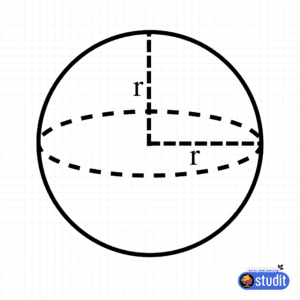
- Sphere: A round 3D shape where every point on the surface is equidistant from the center, like a basketball or a globe.

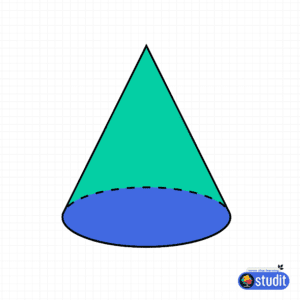
- Cone: A 3D shape with a single circular base and one vertex, like an ice cream cone or a traffic cone.

- Cylinder: A 3D shape with two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface, like a soda can or a drum.

Properties of 3D Shapes
Each 3D shape has unique features based on its faces, edges, and vertices. Here’s a quick overview of common 3D shapes and their properties:
| 3D Shape | Faces | Edges | Vertices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cube | 6 (square) | 12 | 8 |
| Cuboid | 6 (rectangular) | 12 | 8 |
| Cone | 2 (1 circular base, 1 curved surface) | 1 | 1 |
| Cylinder | 3 (2 circular bases, 1 curved surface) | 2 | 0 |
| Sphere | 1 (curved surface) | 0 | 0 |
| Square-based Pyramid | 5 (1 square base, 4 triangular faces) | 8 | 5 |
| Triangular Prism | 5 (2 triangular bases, 3 rectangular faces) | 9 | 6 |
Need help memorizing these? Studit’s personalized tutoring makes it easy for students in Classes 4 to 12!
Surface Area and Volume of 3D Shapes
3D shapes are measured by their surface area (the total area of all faces) and volume (the space they occupy). Here are the key formulas:
| 3D Shape | Total Surface Area (TSA) | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Cube | 6a² (a = edge length) | a³ |
| Cuboid | 2(lw + wh + lh) (l = length, w = width, h = height) | lwh |
| Cone | πr(l + r) (r = radius, l = slant height) | (1/3)πr²h |
| Cylinder | 2πr(h + r) (r = radius, h = height) | πr²h |
| Sphere | 4πr² (r = radius) | (4/3)πr³ |
These formulas are essential for solving geometry problems in CBSE, ICSE, and CHSE exams. Practice them with Studit’s expert tutors!
3D Shapes and Nets
A net is a 2D shape that can be folded to form a 3D shape. Imagine cutting open a box and laying it flat—that’s its net! Here’s how nets work for common 3D shapes:
- Cube: A net of 6 squares arranged in a cross pattern, like unfolding a dice.
- Cuboid: A net of 6 rectangles, like flattening a shoebox.
- Cone: A net with a circular base and a curved sector, like a birthday cap cut open.
- Cylinder: A net with two circles (bases) and a curved rectangle, like unrolling a soda can.
- Square-based Pyramid: A net with a square base and four triangles, like unfolding a pyramid model.
Try making nets at home to understand 3D shapes better! Studit’s tutors can guide you through hands-on activities to master this concept.
Solved Examples
Let’s practice with some questions:
Q1: What is the surface area of a cube with an edge length of 5 cm?
Solution:
Surface area of a cube = 6a²
= 6 × 5² = 6 × 25 = 150 cm²
Answer: The surface area is 150 cm².
Q2: Find the volume of a cylinder with a radius of 4 cm and height of 10 cm. (Use π = 3.14)
Solution:
Volume of a cylinder = πr²h
= 3.14 × 4² × 10 = 3.14 × 16 × 10 = 502.4 cm³
Answer: The volume is 502.4 cm³.
Q3: What is the total surface area of a cone with a radius of 3 cm and slant height of 5 cm? (Use π = 3.14)
Solution:
Total surface area of a cone = πr(l + r)
= 3.14 × 3 × (5 + 3) = 3.14 × 3 × 8 = 75.36 cm²
Answer: The surface area is 75.36 cm².
Need help with these problems? Studit’s tutors in Bhubaneswar offer personalized lessons to make geometry easy!
Learn Geometry with Studit
At Studit, we make learning 3D shapes fun and simple for students in Bhubaneswar and beyond. Whether you’re in Class 3 exploring shapes or in Class 12 preparing for board exams, our expert tutors are here to help. Here’s why Studit is your go-to for mastering geometry:
- Personalized Home Tuition: One-on-one lessons tailored to your learning pace.
- Free Demo Classes: Try our teaching style with no commitment.
- Studit App: Book classes, track progress, and get feedback anytime.
- 24/7 Support: We’re here to answer your questions, day or night.
Ready to conquer 3D shapes and excel in geometry? Visit www.studit.in or download the Studit app to book a free demo class today. Let’s shape your math success!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are 3D shapes in math?
3D shapes, or solids, are objects with length, width, and height, like cubes, cones, and spheres.
Q2: How are 2D and 3D shapes different?
2D shapes are flat with only length and width, while 3D shapes have depth, making them solid.
Q3: What are the properties of 3D shapes?
3D shapes have faces (flat or curved surfaces), edges (lines where faces meet), and vertices (points where edges meet).
Q4: What is a net in geometry?
A net is a 2D shape that can be folded to form a 3D shape, like a flattened cube or cone.
Q5: What are real-life examples of 3D shapes?
Examples include a basketball (sphere), a juice can (cylinder), an ice cream cone (cone), and a box (cuboid).
Q6: Why are 3D shapes important for exams?
Understanding 3D shapes helps solve problems on surface area, volume, and nets, key topics in CBSE, ICSE, and state board syllabi.